To order these parts you must work up the part number by combining the options you want. Their web page gives all the particulars. We do recommend the sealed housings to help keep out moisture. For the Azimuth encoder we recommend the A2-S-B-D-M-S. The part number was derived as follows: Series = A2, S = SEI buss, B = Ball Bearing, D = Default shaft extension, M = Includes mounting plate, S = Sealed Housing. Note 1.
For the inclinometer the part number is A2T-S-D-S. Series = A2T, S = SEI buss, D = Double Damping, S = Sealed housing.
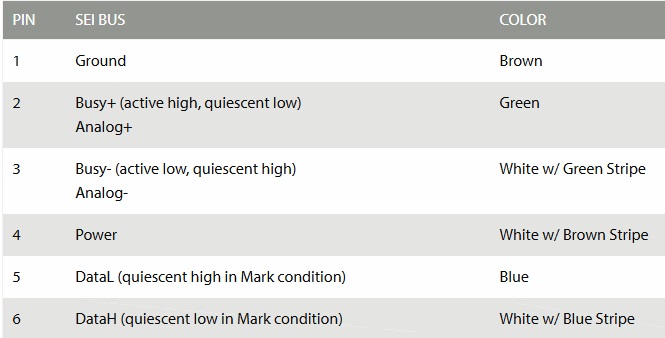
When you buy A2 encoders, you can order wires with connectors in the length you need (see the cable information below).. The connector on the wire kit will plug directly into J1 on the CT-2. If you are using the absolute encoders for both azimuth and elevation then you will need 3 of the wires and a 'Y' adaptor. Note 2.
 The 'Y'
combines the signals from each of the encoders. You will need to
determine the needed length for each side of the 'Y' as well as the
length of the main line.
The 'Y'
combines the signals from each of the encoders. You will need to
determine the needed length for each side of the 'Y' as well as the
length of the main line.
Alternatively you can buy wire, connectors and a crimp tool for RJ12 connectors and make up the wiring yourself. You will still need the Y adaptor if you are using two A2 encoders.
Note 1: US Digital has eliminated the option to order encoders with a sealed housing. So the new part number for the A2 encoder is A2-S-B-D-M-D, and A2T-S-D-D for the inclinometer.
Note 2: US Digital does not seem to carry the Y adaptors any more. Maybe they do but not on their web pages. I found some on Amazon, but could not link the page here. Be very careful when ordering, the part must be specified as 6P6C for six wire connectors. Most Y adaptors on the market are for 4 pins and will not work for the absolute encoders.